Khavari Lab

Publications
Publications
SELECTED RECENT PUBLICATIONS
For a full list of Khavari lab publications please click here
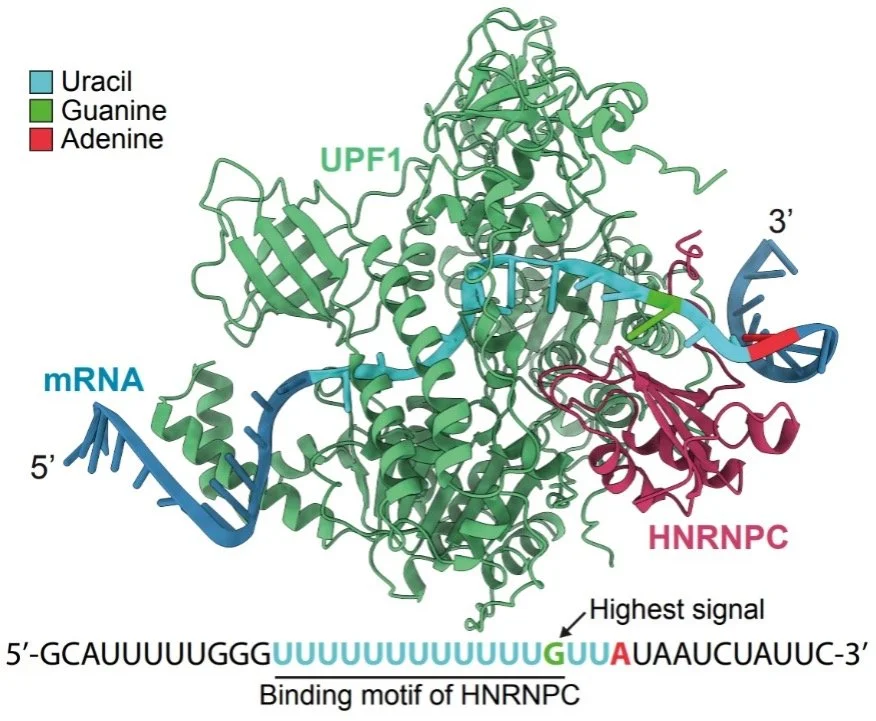
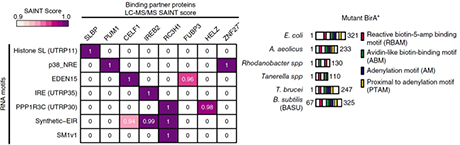
irCLIP-RNP AND Re-CLIP reveal patterns of dynamic protein assemblies on RNA
Ducoli L, Zarnegar BJ, Porter DF, Meyers RM, Miao W, Riley NM, Srinivasan S, Jackrazi LV, Yang Y-Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Bertozzi CR, Flynn RA, Khavari PA. NATURE (2025).
RNA binding proteins (RBPs) control diverse processes, including RNA splicing, stability, transport, and translation. Dysfunctional RNA-RBP interactions contribute to disease, however, the nature and dynamics of multiprotein assemblies on RNA is largely unknown. To address this, non-isotopic ligation-based ultraviolet crosslinking immunoprecipitation was combined with mass spectrometry (irCLIP-RNP) to identify RNA-dependent associated proteins (RDAPs) co-bound to RNA with any RBP of interest. irCLIP-RNP defined landscapes of multimeric protein assemblies on RNA, uncovering previously unknown patterns of RBP-RNA associations, including cell-type-selective combinatorial “RBP codes”. irCLIP-RNP defined dynamic RDAP remodeling in response to EGF, uncovering EGF-induced recruitment of UPF1 adjacent to HNRNPC to effect splicing surveillance of cell proliferation mRNAs. To identify the RNAs simultaneously co-bound by multiple studied RBPs, a sequential immunoprecipitation irCLIP (Re-CLIP) method was also developed. Re-CLIP confirmed binding relationships seen in irCLIP-RNP and identified HNRNPC and UPF1 RBP co-binding on RND3 and DDX3X mRNAs. irCLIP-RNP and Re-CLIP provide a framework to identify and characterize dynamic RNA-protein assemblies in living cells.
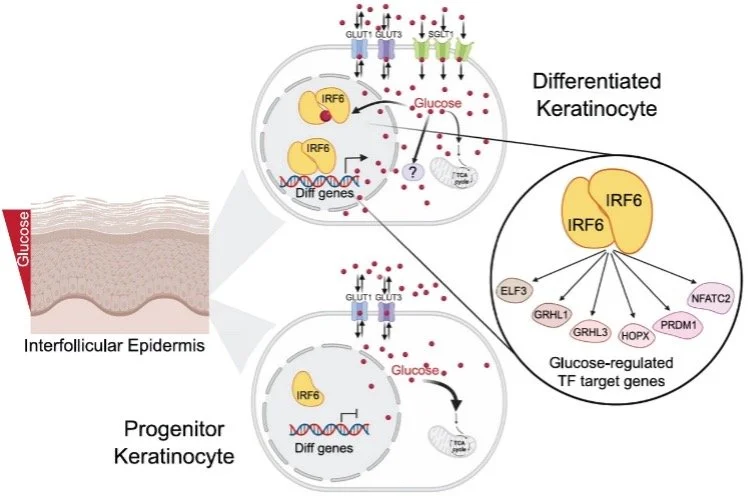
GLUCOSE MODULATES IRF6 TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR DIMERIZATION TO ENABLE EPIDERMAL DIFFERENTIATION
Lopez-Pajares V, Bhaduri A, Zhao Y, Gowrishankar G, Donohue L, Guo MG, Siprashvili Z, Miao W, Nguyen DT, Yang X, Li AM, Tung A, Shanderson RL, Winge MCG, Meservey LM, Srinivasan S, Meyers RMM, Guerrero A, Ji AL, Garcia OS, Tao S, Gambhir, SS, Long JZ, Ye J Khavari PA. CELL STEM CELL (2025).
Non-energetic roles for glucose are largely unclear, as is the interplay between transcription factors (TFs) and ubiquitous small biomolecules. Metabolomic analyses uncovered intracellular glucose elevation during the differentiation of diverse cell types. Human and mouse tissue engineered with glucose sensors detected a glucose gradient that peaked in the outermost differentiated layers of the epidermis. Free glucose accumulation was essential for epidermal differentiation and required the SGLT1 transporter. Glucose affinity chromatography uncovered glucose binding to diverse regulatory proteins, including the IRF6 TF. Direct glucose binding enabled IRF6 dimerization, DNA binding, genomic targeting, and induction of IRF6 target genes, including essential pro-differentiation TFs GRHL1, GRHL3, HOPX, and PRDM1. These data identify glucose as a gradient morphogen that modulates protein multimerization in
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF CANCER-ASSOCIATED GERMLINE RISK VARIANTS
Kellman LN, Neela PH, Srinivasan S, Siprashvili Z, Shanderson RL, Hong AW, Rao D, Porter DF, Reynolds DL, Meyers RM, Guo MG, Yang X, Zhao Y, Wozniak GG, Donohue L, Shenoy R, Ko LA, Nguyen DT, Mondal S, Garcia OS, Elcavage L, Elfaki I, Abell NS, Tao S, Lopez CM, Montgomery SB, Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2025).
Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) in regulatory DNA are linked to inherited cancer risk. Massively parallel reporter assays of 4,041 SNVs linked to 13 neoplasms comprising >90% of human malignancies were performed in pertinent primary human cell types and then integrated with matching chromatin accessibility, DNA looping and expression quantitative trait loci data to nominate 380 regulatory SNVs and their putative target genes. The latter highlighted specific protein networks in lifetime cancer risk, including mitochondrial translation, DNA damage repair and Rho GTPase activity. A CRISPR knockout screen demonstrated that a subset of germline putative risk genes also enable the growth of established human tumors. Editing one cancer-risk linked SNV, rs10411210 , showed that its risk allele increases rhophilin RHPN2 expression and stimulus-responsive RhoA activation, indicating that individual SNVs are capable of functionally upregulating critical cancer-linked pathways. These functional data are a resource for variant prioritization efforts and further interrogation of the mechanisms underlying inherited risk for cancer.
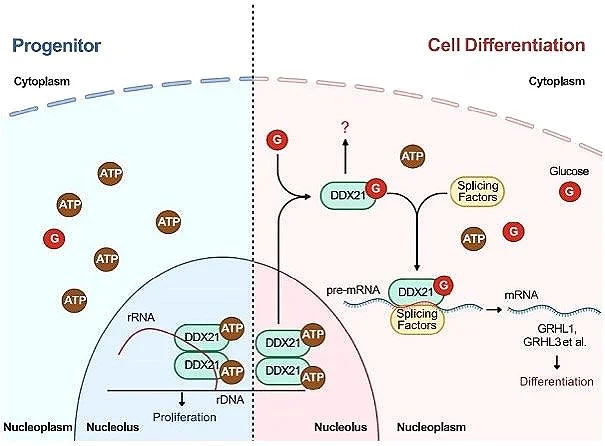
GLUCOSE DISSOCIATES DDX21 DIMERS TO REGULATE mRNA SPLICING AND TISSUE DIFFERENTIATION
Miao W, Porter DF, Lopez-Pajares V, Siprashvili Z, Meyers RM, Bai Y, Nguyen DT, Ko LA, Zarnegar BJ, Ferguson ID, Mills MD, Jilly-Rehak CE, Wu C-G, Yang Y-Y, Meyers JM, Hong AW, Reynolds DL, Ramanathan M, Tao S, Jiang S, Flynn RA, Wang Y, Nolan GP, Khavari PA. CELL (2023).
Glucose, the canonical universal source bioenergy, was found to play a role in controlling protein interactions, including of DEAD-box family RNA helicases. Glucose bound the ATP-binding domain of the DDX21 helicase to mediate its essential role in mRNA splicing genes essential for tissue homeostasis and differentiation.
INTEGRATIVE ANALYSES HIGHLIGHT FUNCTIONAL REGULATORY VARIANTS ASSOCIATED WITH NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISEASES
Guo M, Reynolds DL, Ang C, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Donohue LKH, Siprashvili Z, Yang X, Yoo Y, Mondal S, Hong A, Kain J, Meservey L, Fabo T, Elfaki I, Kellman LN, Abell NS, Pershad Y, Bayat V, Etminani P, Holodniy M, Geschwind DH, Montgomery SB, Duncan LE, Urban AE, Altman RB, Wernig M, Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2023).
Noncoding variants in regulatory DNA contribute to the heritability of polygenic disease, including neuropsychiatric disorders. Epigenomic and transcriptomic data were integrated with massively parallel reporter assays in developing human neural cells to generate a single nucleotide resolution activity map of disease risk and to nominate new pathomechanisms in 10 prevalent neuropsychiatric diseases
ADVANCES IN CUTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
Winge MCG, Kellman LN, Guo K, Tang JY, Swetter SM, Aasi SZ, Sari KY, Chang ALS, Khavari PA. NATURE REVIEWS CANCER (2023).
Human malignancies arise predominantly in tissues of epithelial origin, where the stepwise transformation to invasive neoplasia involves sequential dysregulation of biological networks that govern essential functions of epithelial homeostasis. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is a prototype epithelial malignancy. Recent advances in genetics, single cell analysis, and spatial transcriptomics nominate pathways and cell subpopulations important in pathogenesis.
PROBER IDENTIFIES PROTEINS ASSOCIATED WITH PROGRAMMABLE SEQUENCE-SPECIFIC DNA IN LIVING CELLS
Mondal S, Ramanathan M, Miao W, Meyers RM, Rao D, Lopez-Pajares V, Siprashvili Z, Reynolds DL, Porter DF, Ferguson I, Neela P, Zhao Y, Meservey LM, Guo MG, Yang Y-Y, Wang Y, Khavari PA. NATURE METHODS (2022).
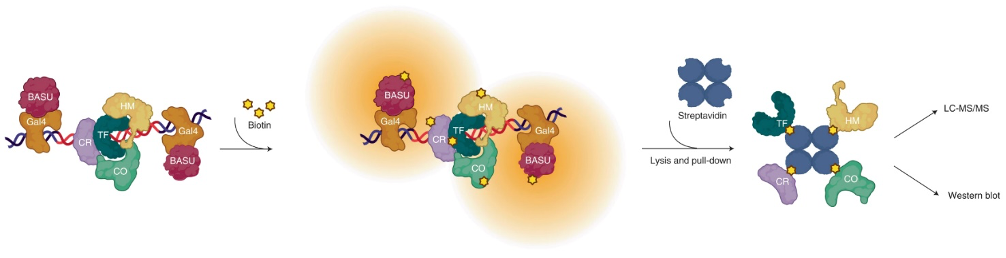
DNA-protein interactions mediate physiologic gene regulation and may be altered by DNA variants linked to polygenic disease. Proximal biotinylation by episomal recruitment (PROBER) was developed to enhance the speed and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the identification and quantification of proteins associated with specific DNA sequences in living cells. PROBER quantified both constitutive and inducible association of transcription factors and chromatin regulators to target DNA sequences as well as binding quantitative trait loci due to single-nucleotide variants. PROBER identified alterations in regulator associations due to cancer hotspot mutations in the hTERT promoter, indicating that these mutations increase promoter association with specific gene activators. PROBER provides an approach to rapidly identify proteins associated with specific DNA sequences and their variants in living cells.
THE DYNAMIC, COMBINATORIAL CIS-REGULATORY LEXICON OF EPIDERMAL DIFFERENTIATION
Kim DS, Risca VI, Reynolds DL, Chapell J, Rubin AJ, Jung N, Donohue LKH, Lopez-Pajares V, Kathiria A, Shi M, Zhao Z, Deep H, Sharmin M, Rao D, Lin S, Chang HY, Synder MP, Greenleaf WJ, Kundaje A, Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2021).
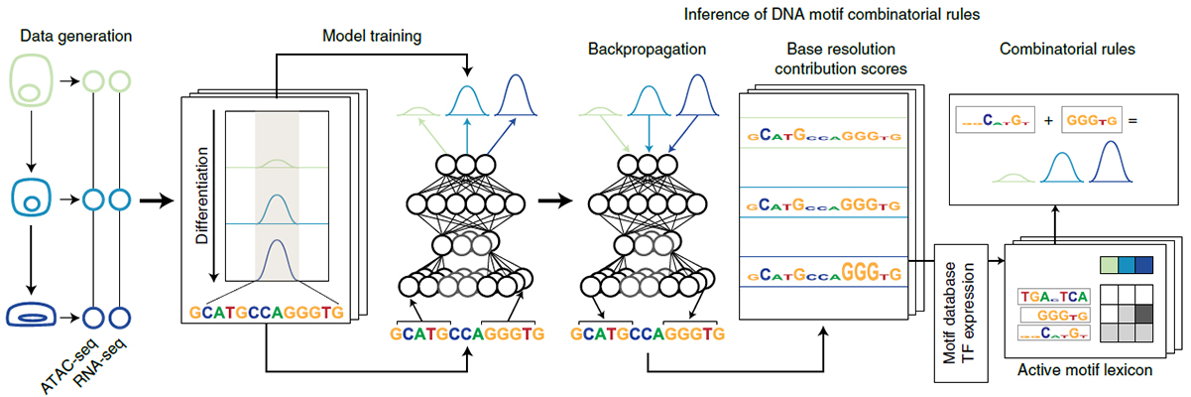
Transcription factors bind DNA sequence motif vocabularies in cis-regulatory elements (CREs) to modulate chromatin states and gene expression during cell state transitions. Multiomic data profiling of chromatin and expression dynamics across epidermal differentiation identified 40,103 dynamic CREs associated with 3,609 dynamically expressed genes. An interpretable deep-learning framework was then used to model the cis-regulatory logic of chromatin accessibility. This analysis framework identified a cooperative cis-regulatory logic regulating synchronous gene modules with diverse roles in skin differentiation, which was validated by massively parallel reporter assays. This integrative approach provides a general framework for deciphering the organizational principles of the cis regulatory code mediating dynamic genome regulation.
INTEGRATING SINGLE-CELL AND SPATIAL TRANSCRIPTOMICS DATA TO ELUCIDATE INTERCELLAR TISSUE DYNAMICS
Longo SK, Guo MG, Ji AL, Khavari PA. NATURE REVIEWS GENETICS (2021).
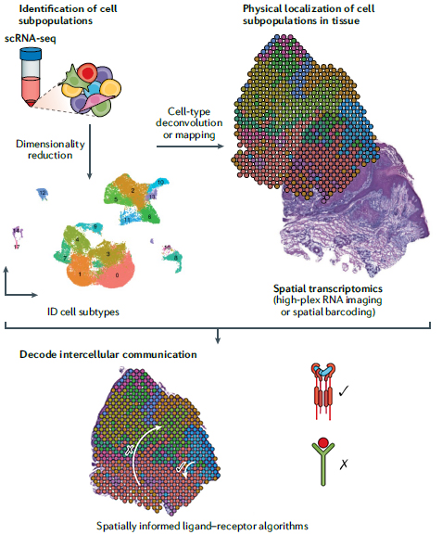
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) identifies cell subpopulations within tissue but does not capture their spatial distribution nor reveal local networks of intercellular communication acting in situ. Spatial transcriptomics (ST) permits high-plex RNA imaging in tissue and can thus help address this challenge. ST methodologies comprise a suite of recently developed techniques that localize RNA within tissue and include multiplexed in situ hybridization, in situ sequencing, and spatial barcoding. However, no method currently provides as complete a scope of the transcriptome as does scRNA-seq, underscoring the need for approaches to integrate single-cell and spatial data. New efforts are designed to integrate scRNA-seq with spatial transcriptomics technologies, including emerging integrative computational methods that effectively combine current methodologies.
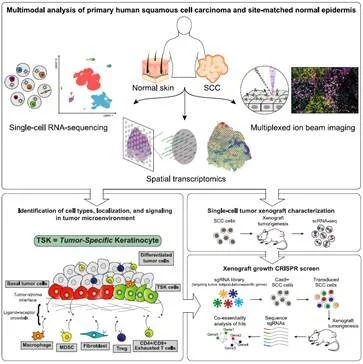
MULTIMODAL ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITION AND SPATIAL ARCHITECTURE OF HUMAN SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
Ji AL, Rubin AJ, Thrane K, Jiang S, Reynolds DL, Meyers, RM, Guo MG, George BM, Molbrink A, Bergenstrahle J, Larsson L, Bai Y, Zhu B, Bhaduri A, Meyers JM, Rovira-Clave X, Hollmig SH, Aasi, SZ, Nolan GP, Lundeberg J, Khavari PA. CELL (2020).
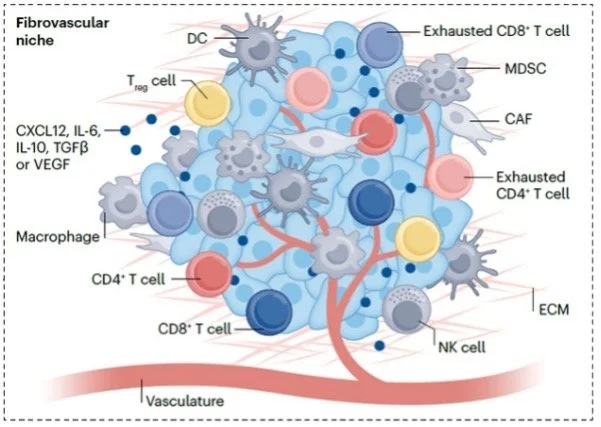
Diseased tissues, including cancer, are comprised of heterogeneous cell types with discrete architectural features. To define all cell subpopulations in tumors, and how they are configured in 3-dimensional space, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), was studied with single cell RNA-seq, spatial transcriptomics, and multiplex ion beam imaging. cSCC exhibited 4 tumor subpopulations, 3 recapitulating normal epidermis, and a tumor-specific keratinocyte (TSK) population unique to cancer. TSKs expressed a genetic program linked to poorer outcomes across diverse human epithelial cancers and were spatially localized to a specific fibrovascular niche at the tumor-stroma border. Integration of single-cell and spatial data mapped ligand-receptor networks to specific cell types, revealing TSK cells as a hub for intercellular communication. This work defined cancer tumor and stromal cell subpopulations, the spatial niches where they interact, and the communicating gene networks that they engage in cancer.
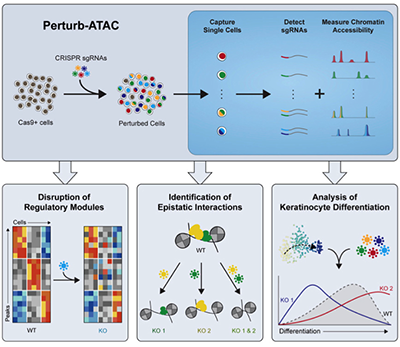
COUPLED SINGLE-CELL CRISPR SCREENING AND EPIGENOMIC PROFILING REVEALS CAUSAL GENE REGULATORY NETWORKS
Rubin AJ, Parker KR, Satpathy AT, Qi Y, Wu B, Ong AJ, Mumbach MR, Ji AL, Kim DS, Cho SW, Zarnegar BJ, Greenleaf WJ, Chang HY, Khavari PA. CELL (2019).
Perturb-ATAC, combines multiplexed CRISPRi or knockout with genome-wide chromatin accessibility profiling in single cells via simultaneous detection of sgRNAs and open chromatin sites by assay of transposase-accessible chromatin with sequencing (ATAC-seq). Perturb-ATAC application to transcription factors (TFs), chromatin regulators, & noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in ∼4,300 single cells, encompassed more than 63 genotype-phenotype relationships. This uncovered regulators of chromatin accessibility, TF occupancy, and nucleosome positioning and identified a hierarchy of TFs that govern cell state, variation, and disease-associated cis-regulatory elements. Perturb-ATAC in epidermal cells revealed 3 sequential of cis-element modules encoding keratinocyte fate. Combinatorial deletion of all pairs of these TFs uncovered their epistatic relationships and highlighted genomic co-localization as a basis for synergy. Perturb-ATAC is a powerful strategy to dissect gene regulatory networks in development and disease.
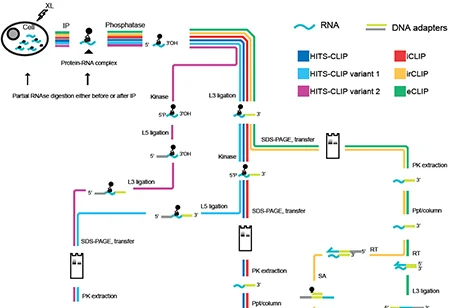
METHODS TO STUDY RNA-PROTEIN INTERACTIONS
Rahmanathan M,* Porter DF,* Khavari PA. NATURE METHODS (2019).
Noncoding RNA sequences, including long noncoding RNAs, small nucleolar RNAs, and untranslated mRNA regions, accomplish many of their diverse functions through direct interactions with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs). The full spectrum of potential RNA-protein interactions within living cells, however, has not yet been defined. This represents a significant gap in knowledge relevant to a host of biological process, including stem cell differentiation and cancer. Recent efforts have identified hundreds of new RBPs that lack known RNA-binding domains, thus underscoring the complexity and diversity of potential RNA-protein complexes. Recent progress has expanded the number of methods for studying RNA-protein interactions in two general categories: approaches that characterize proteins bound to an RNA of interest (RNA-centric), and those that examine RNAs bound to a protein of interest (protein-centric). Each method has unique strengths and limitations, which makes it important to select optimal approaches for the biological question being addressed. This paper reviews methods for the study of RNA-protein interactions, with a focus on their suitability for specific applications.
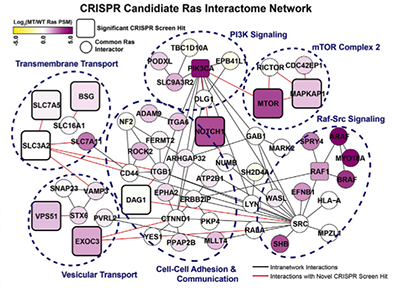
THE FUNCTIONAL PROXIMAL PROTEOME OF ONCOGENIC RAS INCLUDES mTORC2
Kovalski JR, Bhaduri A, Zehnder AM, Neela PH, Che Y, Wozniak GG, Khavari PA. MOLECULAR CELL (2019).
Proximity-dependent biotin labeling (BioID) may identify new targets for cancers driven by difficult-to-drug oncogenes, such as Ras. BioID was therefore used with wild-type (WT) and oncogenic mutant (MT) H-, K-, and N-Ras, identifying known interactors, including Raf and PI3K, as well as a common set of 130 novel proteins proximal to all Ras isoforms. A CRISPR screen of these proteins for Ras-dependence identified mTOR, which was also found proximal to MT Ras in human tumors. Oncogenic Ras directly bound two mTOR Complex 2 (mTORC2) components, mTOR and MAPKAP1, to promote mTORC2 kinase activity at the plasma membrane. mTORC2 enabled the Ras pro-proliferative cell cycle transcriptional program and perturbing the Ras-mTORC2 interaction impaired Ras-dependent neoplasia in vivo. Combining proximity-dependent proteomics with CRISPR screening identified a new set of functional Ras-associated proteins, defined mTORC2 as a new direct Ras effector, and offers a strategy for finding new proteins that cooperate with dominant oncogenes.
RNA-PROTEIN INTERACTION DETECTION IN LIVING CELLS
Ramanathan M, Maizoub K, Rao DS, Neela PH, Zarnegar BJ, Mondal S, Roth JG, Gai J, Kovalski JR, Siprashvili Z, Palmer TD, Carette JE, Khavari PA. NATURE METHODS (2018).
RNA-protein interaction detection (RAPID) tethers enhanced proximity proteomics to RNA to rapidly identify the proteins that bind any RNA sequence of interest in living cells. RAPID defined protein binding to mutant RNA motifs in human genetic disorders, uncovered potential post-transcriptional networks in breast cancer, and discovered essential host proteins that interact with Zika virus RNA. This new methodology enables direct study of RNA-protein interactions in living cells and tissues on a timescale of minutes to accelerate the growing field of RNA proteomics.
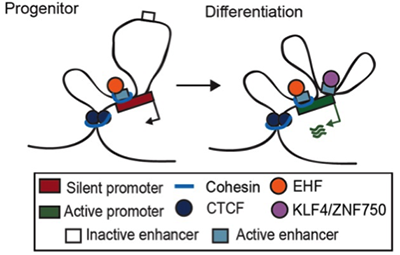
LINEAGE-SPECIFIC DYNAMIC AND PRE-ESTABLISHED ENHANCER-PROMOTER CONTACT COOPERATE IN TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION.
Rubin AJ, Barajas BC, Furlan-Magaril M, Lopez-Pajares V, Mumbach MR, Howard I, Kim DS, Boxer LD, Cairns J, Spivakov M, Wingett SW, Shi M, Zhao Z, Greenleaf WJ, Kundaje A, Snyder M, Chang HY, Fraser P, Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2017).
A kinetic study of 3D chromatin dynamics across the genome of normal progenitor cells undergoing terminal differentiation identified two types of transcriptional enhancers in contact with target genes. Constitutive enhancers are pre-looped, H3K27ac-marked, and cohesin-bound while dynamic enhancers gain H3K27ac activation marks and loop to target genes only during differentiation. Distinctive sets of transcription factor (TF) bind each enhancer class and this work discovered EHF as a new essential TF required for constitutive enhancer function in this setting. These new features of genome regulation during stem cell differentiation underscore the diversity of mechanism engaged during this process.
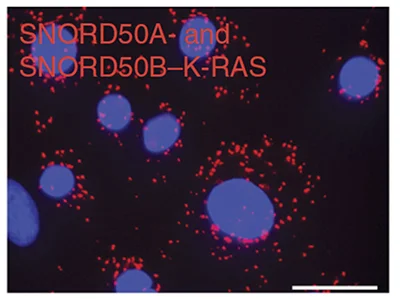
THE NONCODING RNAs SNORD50A AND SNORD50B BIND K-Ras AND ARE RECURRENTLY DELETED IN HUMAN CANCER.
Siprashvili Z, Webster DE, Johnston D, Shenoy R, Ungewickell A, Bhaduri A, Flockhart R, Zarnegar BJ, Che Y, Meschi F, Puglisi JD & Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2016).
To help define roles for specific small noncoding snoRNAs in cancer, we analyzed 5,473 pairs of tumor and matching normal genomes in 21 human cancer types to discover recurrent deletion of SNORD50A/B in 26% of human tumors. CRISPR knockouts in tumor cells combined with new methodologies to analyze RNA-protein interactions characterized SNORD50A/B as a Ras-binding tumor suppressor RNA that inhibits Ras function by altering its post-translational modification. Small noncoding RNAs therefore can play dominant roles in cancer by binding oncogenes and altering their function.
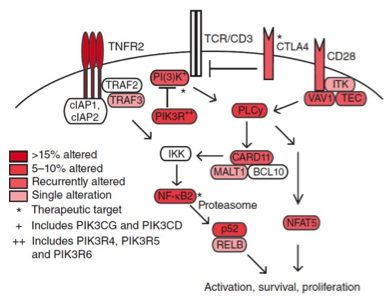
GENOMIC ANALYSIS OF MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES AND SÉZARY SYNDROME IDENTIFIES RECURRENT ALTERATIONS IN TNFR2.
Ungewickell A, Bhaduri A, Rios E, Reuter J, Lee CS, Mah A, Zehnder A, Ohgami R, Kulkarni S, Armstrong R, Weng WK, Gratzinger D, Tavallaee M, Rook A, Snyder M, Kim Y & Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2015).
Cancer is characterized by enhanced cellular proliferation in concert with increased resistance to cell death. The mechanisms whereby stem cells undergoing malignant transformation achieve these dual aberrations, however, are highly diverse, depending on tissue and tumor type. Here we use high throughput sequencing to identify recurrent induction of cell survival and activation pathways in cutaneous T cell lymphoma.
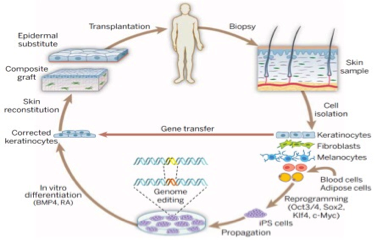
ADVANCES IN SKIN GRAFTING AND TREATMENT OF CUTANEOUS WOUNDS.
Sun BK, Siprashvili Z & Khavari PA. SCIENCE (2014).
Tissue regeneration after injury is essential for survival. Advances in stem cell biology, genome editing, and tissue regeneration have laid the foundation for new approaches to cutaneous regeneration and grafting. Cas9 gene-edited somatic cells and iPS cells may be used in this process for the treatment of a host of monogenic disorders, such as epidermolysis bullosa (EB).
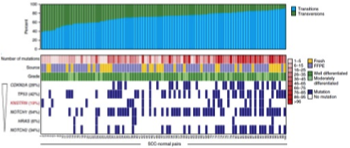
RECURRENT POINT MUTATIONS IN THE KINETOCHORE GENE KNSTRN IN CUTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA.
Lee CS, Bhaduri A, Mah A, Johnson WL, Ungewickell A, Aros CJ, Nguyen CB, Rios EJ, Siprashvili Z, Straight A, Kim J, Aasi SZ & Khavari PA. NATURE GENETICS (2014).
Epithelial neoplasms, which comprise ~90% of human cancers, are characterized by widespread genome damage by mechanisms that are incompletely understood. Here we used high throughput genome sequencing to define recurrent mutations in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), the second most common cancer in humans. SCC displays hotspot mutations in the KNSTRN gene that trigger aneuploidy and accelerate tumorigenesis, identifying a new common mechanism of genomic injury in cancer.
IQGAP1 SCAFFOLD-KINASE INTERACTION BLOCKADE SELECTIVELY TARGETS RAS-MAP KINASE-DRIVEN TUMORS.
Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J, Zarnegar B, Sage J & Khavari PA. NATURE MEDICINE (2013).
Hyperactive signaling of the Ras-Erk1/2 MAPK pathway occurs commonly in cancer, however, complete pathway ablation is lethal, underscoring the need for new selective targeting approaches. Scaffold proteins, such as IQGAP1, specify signaling output by assembling pathway components, such as Raf, Mek, and Erk kinases. Here we demonstrate that IQAP1 scaffold-kinase inhibition (SKIB) – by selectively disrupting Erk1/2 pathway assembly in cancer - represents a promising new approach to molecular oncology therapy.
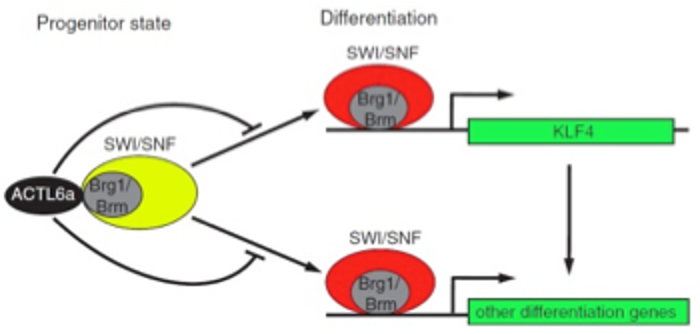
ACTL6a ENFORCES THE EPIDERMAL PROGENITOR STATE BY SUPPRESSING SWI/SNF-DEPENDENT INDUCTION OF KLF4.
Bao X, Tang J, Lopez-Pajares V, Tao S, Qu K, Crabtree GR & Khavari PA. CELL STEM CELL (2013).
Somatic stem cells suppress differentiation to maintain tissue self-renewal. Chromatin remodelers, such as the BAF (SWI/SNF) complex, control nucleosome positioning to modulate genome expression. Here we identify a selective role for the ACTL6A BAF chromatin remodeler subunit in stem cell maintenance. ACTL6A blocks BAF-mediated activation of KLF4, a TF best known for iPS cell induction whose essential role in mammals in vivo involves induction of terminal epidermal differentiation.
CONTROL OF SOMATIC TISSUE DIFFERENTIATION BY THE LONG NON-CODING RNA TINCR.
Kretz M, Siprashvili Z, Chu C, Webster DE, Zehnder A, Qu K, Lee CS, Flockhart RJ, Groff A, Chow J, Johnston D, Kim G, Spitale RC, Flynn RA, Zheng G, Aiyer S, Raj A, Rinn JL, Chang HY & Khavari PA. NATURE (2013).
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) act by a host of mechanisms to impact genomic expression. To identify lncRNAs with essential roles in differentiation, we undertook a systematic screen to identify Terminal differentiation Induced NonCoding RNA (TINCR). TINCR controlled expression of hundreds of genes by a novel post-transcriptional mechanism that involved complementary base pairing by TINCR to target mRNAs through a 25nt “TINCR” box sequence. TINCR stabilized bound differentiation gene mRNAs in concert with the Staufen 1 protein, demonstrating an entirely new mechanism for lncRNA action.